Sanpress Inox G
Product information
Sanpress Inox G
Press connector system made of stainless steel with stainless steel pipes
| Year built (from): | 20/02/2004 |
Trade mark rights exist for this document; for further information, go to viega.com/legal .
Target groups
The information in this instruction manual is directed at the following groups of people:
Contract installers
Professional companies specialising in the construction, maintenance and alteration of a natural or liquid gas system
Liquid gas systems may only be constructed, maintained or altered by companies that have the necessary qualification and experience.
Individuals without the abovementioned training or qualification are not permitted to mount, install and, if required, maintain this product. This restriction does not extend to possible operating instructions.
The installation of Viega products must take place in accordance with the general rules of engineering and the Viega instructions for use.
Labelling of notes
Warning and advisory texts are set aside from the remainder of the text and are labelled with the relevant pictographs.

DANGER!
This symbol warns of possible life-threatening injury.

WARNING!
This symbol warns of possible serious injury.

CAUTION!
This symbol warns of possible injury.

NOTICE!
This symbol warns of possible damage to property.
INFO!
This symbol gives additional information and hints.
About this translated version
This instruction for use contains important information about the choice of product or system, assembly and commissioning as well as intended use and, if required, maintenance measures. The information about the products, their properties and application technology are based on the current standards in Europe (e.g. EN) and/or in Germany (e.g. DIN/DVGW).
Some passages in the text may refer to technical codes in Europe/Germany. These should serve as recommendations in the absence of corresponding national regulations. The relevant national laws, standards, regulations, directives and other technical provisions take priority over the German/European directives specified in this manual: The information herein is not binding for other countries and regions; as said above, they should be understood as a recommendation.
 | These instructions for use contain videos Some assembly and action steps are shown using the example of a piping system other than the one described here, but are equally applicable. |
Standards and regulations
The following standards and regulations apply to Germany / Europe and are provided as a support feature.
Regulations from section: Application areas
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Planning, execution, modification and operation of gas installations | DVGW-TRGI 2018 |
Planning, execution, modification and operation of liquid gas installations | DVFG-TRF 2021 |
Regulations from section: Media
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Suitability for gases Liquid gas in the gaseous state | DVGW-Arbeitsblatt G 260 |
Suitability for fuel oil | DIN 51603‑1 |
Suitability for diesel fuel | DIN EN 590 |
Regulations from section: Pipes
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Stainless steel pipes with material number 1.4401 | DIN EN 10088 |
Stainless steel pipes with material number 1.4401 | DVGW-Arbeitsblatt GW 541 |
Rules of the fixing technology for gas installations | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.3.7 |
Rules of the fixing technology for gas installations | DVFG-TRF 2021, Point 7.3.6 |
Regulations from section: Corrosion
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
(Subsequent) corrosion protection for underground installation | DIN 30672 |
Corrosion protection for external pipes | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.2.7.1 |
Corrosion protection for internal pipelines | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.2.7.2 |
Corrosion protection for external pipes | DVFG-TRF 2021, Point 7.2.7.1 |
Corrosion protection for internal pipelines | DVFG-TRF 2021, Point 7.2.7.2 |
Overground pipelines in recesses in the bare floor or levelling layer | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.3.7.8.4 |
Regulations from section: Storage
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Requirements for material storage | DIN EN 806‑4, Chapter 4.2 |
Regulations from section: Notes on mounting
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
The general rules of mounting for gas installations | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.3.7 |
Regulations from section: Establishing a flange connection
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Qualification of personnel for the assembly of flange connections | VDI-Richtlinie 2290 |
Determination of tightening torques | DIN EN 1591‑1 |
Regulations from section: Leakage test
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Leakage test for gas installations | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Point 5.6 |
Testing and initial commissioning of a liquid gas system | DVFG-TRF 2021, Point 8 |
Regulations from section: Maintenance
Scope / Notice | Regulations applicable in Germany |
|---|---|
Ensuring and maintaining a safe operating condition of gas installations | DVGW-TRGI 2018, Appendix 5c |
Intended use

INFO!
Agree the use of the system for areas of application and media other than those described with Viega.
Areas of application
Use is possible in the following areas among others:
Gas installations, see Regulations from section: Application areas
Liquid gas installations, also see Regulations from section: Application areas .
Heating oil pipelines
Diesel pipes
Compressed air systems
Gas installation
For planning, execution, modification and operation of gas installations, observe the applicable regulations, see Regulations from section: Application areas .
Use is possible in the gas installations described below:
Gas installations
Low pressure range ≤ 100 hPa (100 mbar)
Medium pressure range from 100 hPa (100 mbar) up to 0.1 MPa (1 bar)
Industrial, commercial and technical processing systems with the corresponding directives and technical regulations up to 0.5 MPa (5 bar)
Liquid gas installations
With liquid gas tank in medium pressure range downstream of the pressure regulating valve, 1st level on the liquid gas tank > 100 hPa (100 mbar) up to a permitted operating pressure of 0.5 MPa (5 bar)
With liquid gas tank in the low pressure range ≤ 100 hPa (100 mbar) behind the pressure regulating valve, 2nd level
With liquid gas pressurised container (liquid gas bottles) < 16 kg
Behind the small bottle pressure regulating valve
With liquid gas tank (liquid gas bottle) ≥ 16 kg
Behind the large bottle pressure regulating device
Media
The system is suitable for the following media, amongst others:
For the applicable directives, see Regulations from section: Media .
Gases
Liquid gases, only in the gaseous state for domestic and commercial applications
Heating oil
Diesel fuel
Compressed air
Product description
Overview
The piping system consists of press connectors in connection with stainless steel pipes and the corresponding press tools.
The system components are available in the following dimensions: d15 / 18 / 22 / 28 / 35 / 42 / 54.
Pipes
Only 1.4401 Sanpress stainless steel pipes or stainless steel pipes according to the valid regulations with the material number 1.4401 may be used, see Regulations from section: Pipes .
The following pipe is available from the system described:
Type of pipe |
|---|
d |
Areas of application |
Material No. |
PRE value |
Pipe marking |
Protective cap |
Stainless steel pipe 1.4401 |
|---|
15 / 18 / 22 / 28 / 35 / 42 / 54 |
Potable water and gas installations1) |
1.4401 (X5CrNiMo 17‑12-2), with 2.3 % molybdenum for increased durability |
24.1 |
— |
Yellow |
| 1) | Gas installations only in connection with Sanpress Inox G and Profipress G press connectors (only up to d 28) |
Pipe key data Sanpress pipe (1.4401)
d x smin [mm] | Volume per metre of pipe [l/m] | Pipe weight [kg/m] |
|---|---|---|
15 x 1.0 | 0.13 | 0.35 |
18 x 1.0 | 0.20 | 0.43 |
22 x 1.2 | 0.30 | 0.65 |
28 x 1.2 | 0.51 | 0.84 |
35 x 1.5 | 0.80 | 1.26 |
42 x 1.5 | 1.19 | 1.52 |
54 x 1.5 | 2.04 | 1.97 |

NOTICE!
Do not use adhesive tape to pack the pipes. Remove adhesive residues from the pipe without leaving any residue.
Laying and fixing pipes
Only pipe clamps with chloride-free sound insulating inlays should be used to secure the pipes.
Observe the general rules of fixing technology:
For gas installations, see Regulations from section: Pipes .
Only fix on components with sufficient stability.
Gas supply lines must not be secured to other pipelines nor should they be used as support for other pipelines.
The system can be secured using commercially available plastic dowels together with non-flammable pipe clamps (e. g. metallic pipe clamps).
For gas supply lines, the following fixing intervals must be observed for pipelines laid horizontally:
Distance between the pipe clamps
d [mm] | Fixing distance between |
|---|---|
15.0 | 1.25 |
18.0 | 1.50 |
22.0 | 2.00 |
28.0 | 2.25 |
35.0 | 2.75 |
42.0 | 3.00 |
54.0 | 3.50 |
Press connectors
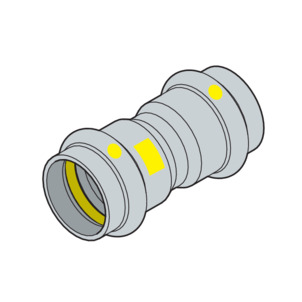
The press connectors have a circumferential bead in which the sealing element lies. The press connector is deformed upstream and downstream of the bead and permanently connected to the pipe during pressing. The sealing element is not deformed during pressing.
SC‑Contur
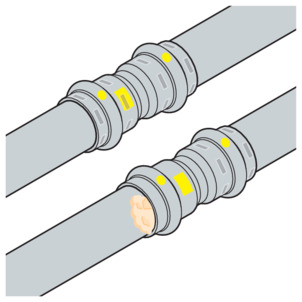
Viega press connectors are equipped with the SC‑Contur. The SC‑Contur is a safety technology that is certified by the DVGW and ensures that the press connector is guaranteed to be leaky in an unpressed state. In this way, inadvertently unpressed connections are noticed during a leakage test.
Viega guarantees that unpressed connections become visible during a leakage test:
with dry leakage test in the pressure range from 22 hPa–0.3 MPa (22 mbar–3.0 bar)
Sealing elements
Use |
|---|
Operating temperature |
Operating pressure |
Gas installation | Liquid gas installation | Heating oil and diesel pipelines |
|---|---|---|
-20 °C up to 70 °C | -20 °C up to 70 °C | ≤ 40 °C |
≤ 0.5 MPa (5 bar) (MOP 5) ≤ 0.5 MPa (5 bar) (HTR / GT5)1) | ≤ 0.5 MPa (5 bar) (MOP 5) ≤ 0.5 MPa (5 bar) (HTR / GT5)1) | ≤ 0.5 MPa (5 bar) |
| 1) | Operating pressure at HTR requirement max. 0.5 MPa (5 bar) (GT5) |
Markings on components
Pipe marking
The pipe markings contain important information regarding the material configuration and manufacture of the pipes. Their meaning is as follows:
Manufacturer
System name
Pipe material
Certification
Dimension
Supplier's mark
Date of manufacture
Batch number
CE marking
DOP and DOP number
Manufacturing standard
Markings on press connectors
The press connectors are marked with a coloured dot. The dot identifies the SC‑Contur where the test medium would escape in the case of an inadvertently unpressed connection.

The press connectors are marked as follows:
Yellow dot and yellow rectangle for gas
Gas for gas supply lines
MOP5 for maximum operating pressure 0.5 MPa (5 bar)
GT5 for maximum operating pressure with HTR requirement 0.5 MPa (5 bar)
DVGW
SVGW
Information for use
Corrosion
Depending on the area of use, corrosion protection measures may have to be taken into account. One differentiates between external pipelines (underground and overground external pipelines), as well as internal pipelines.
Information about the area of use, also see Areas of application .
The pertinent guidelines must be observed for corrosion protection, see Regulations from section: Corrosion .
Overground pipes and fittings in rooms do not normally require external corrosion protection.
There are exceptions in the following cases:
There is external contact with materials containing chloride.
Stainless steel pipes must not come into contact with building materials or mortar containing chloride.
in aggressive surroundings
In recesses within bare floors or in the compensating layer, they must be treated in the same way as buried external pipelines, see Regulations from section: Corrosion .
Handling
Transport
Observe the following when transporting pipes:
Do not pull the pipes over the sill. The surface could be damaged.
Secure pipes during transportation. Pipes may become bent due to shifting.
Do not damage the protective caps on the pipe ends and do not remove them until immediately before mounting. Damaged pipe ends must not be pressed.
Storage
For storage, comply with the requirements specified in the applicable regulations, see Regulations from section: Storage :
Store components in a clean and dry place.
Do not store the components directly on the floor.
Provide at least three points of support for the storage of pipes.
Where possible, store different sizes separately.
Store small sizes on top of larger sizes if separate storage is not possible.
Only use stainless steel cleaning agent to clean surfaces.
Store pipes of different materials separately to prevent contact corrosion.
Store the seals in such a way that they cannot be damaged by external forces.
Assembly information
Mounting instructions
Checking system components
System components may, in some cases, have become damaged through transportation and storage.
Check all parts.
Replace damaged components.
Do not repair damaged components.
Contaminated components may not be installed.

NOTICE!
Active and possibly passive protection measures are required to protect a gas installation from tampering by unauthorised persons, see Regulations from section: Notes on mounting .
Active protective measures (e. g. gas flow monitor) must always be taken.
Passive protective measures (e.g. gas safety plugs and caps) must be selected and employed depending on the installation.
The general rules of mounting for gas supply lines
The following conditions amongst others are valid when laying gas supply lines:
Lay gas supply lines with clearance from the installation body, concealed without hollow spaces, or in ventilated ducts or shafts.
Do not install gas supply lines with operating pressures > 100 hPa (100 mbar) concealed in the wall.
Arrange gas supply lines in such a way that condense water or water dripping from other pipes and components does not affect them.
Do not lay gas supply lines in screed.
Shut-off systems and detachable connections must be easily accessible.
Requirements on concealed installations:
Lay stress-free.
Apply corrosion protection.
Do not use any detachable connections (screw fittings).

INFO!
Continuous, connection-free gas supply lines may be laid in hollow spaces (pre-wall constructions) to be connected to a gas device or a gas socket.
Ventilation is not required.
Permitted exchange of sealing elements

INFO!
Important instruction
With their material-specific qualities, sealing elements in press connectors are adapted for use with the corresponding media and/or the areas of use of the piping systems and are generally only certified for them.
The exchange of a sealing element is generally permitted. The sealing element must be replaced by a sealing element of the same material Sealing elements . The use of other sealing elements is not permitted.
If the sealing element in the press connector is obviously damaged, it should be exchanged for a Viega spare sealing element made of the same material.
Space requirements and intervals
Pressing between pipelines
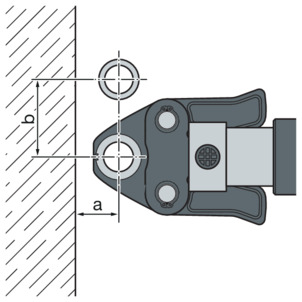
Space required PT1, Type 2 (PT2), PT3-EH, PT3-AH, Pressgun 4B, 4E, 5, 6, 6 Plus
d |
|---|
a [mm] |
b [mm] |
15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 45 | 50 |
50 | 55 | 60 | 70 | 85 | 100 | 115 |
Space requirement Picco, Pressgun Picco, Pressgun Picco 6, Pressgun Picco 6 Plus
d |
|---|
a [mm] |
b [mm] |
15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
60 | 60 | 65 | 65 | 65 |
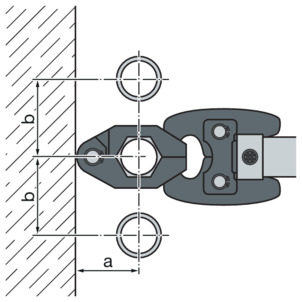
Space requirement press ring
d |
|---|
a [mm] |
b [mm] |
15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
40 | 45 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
50 | 55 | 60 | 70 | 75 | 85 | 90 |
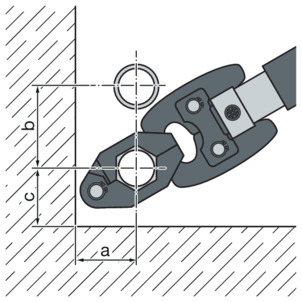
Pressing between pipe and wall
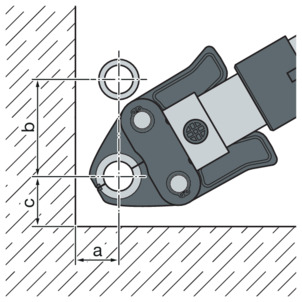
Space requirement Picco, Pressgun Picco, Pressgun Picco 6, Pressgun Picco 6 Plus
d |
|---|
a [mm] |
b [mm] |
c [mm] |
15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
70 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 80 |
40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
Space requirement press ring
d |
|---|
a [mm] |
b [mm] |
c [mm] |
15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 54 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
40 | 45 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 |
50 | 55 | 60 | 70 | 75 | 85 | 90 |
35 | 40 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 65 |
Wall distance
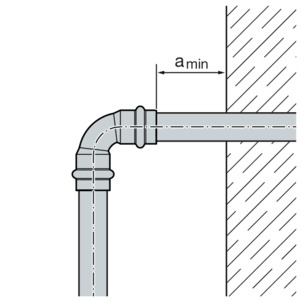
Minimum distance with d 15–54
Press machine |
|---|
PT1 |
Type 2 (PT2) |
Type PT3-EH |
Type PT3-AH |
Pressgun 4E / 4B |
Pressgun 5 |
Pressgun 6 / 6 Plus |
Picco / Pressgun Picco |
Pressgun Picco 6 / Pressgun Picco 6 Plus |
amin [mm] |
|---|
45 |
50 |
35 |
Interval between the pressings

NOTICE!
Leaking press connections due to pipes being too short!
If two press connectors are to be mounted onto a pipe at a short distance apart,, the pipe must not be too short. If the pipe is not inserted up to the prescribed insertion depth in the press connector during pressing, the connection may become leaky.
With pipes with a diameter of d 15–28, the length of the pipe must be at least as long as the total insertion depth of both press connectors.
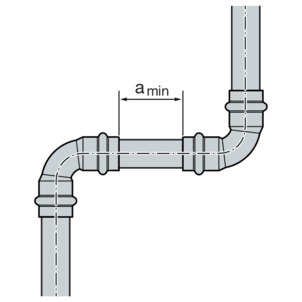
Minimum distance with press jaws d 15–54
d |
|---|
15 |
18 |
22 |
28 |
35 |
42 |
54 |
amin [mm] |
|---|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
25 |
Z dimensions
For the Z dimensions, refer to the respective product page in the online catalogue.
Required tools
The following tools are required for production of a press connection:
Pipe cutter or a fine-toothed hacksaw
Deburrer and coloured pen for marking
Press machine with constant pressing force
Press jaw or press ring with corresponding hinged adapter jaw, suitable for the pipe diameter and with suitable profile

INFO!
Viega recommends the use of Viega system tools when installing the press fittings.
The Viega system press tools have been developed and tailored specifically for the installation of Viega press connector systems.
Assembly
Replacing the sealing element
Removing the sealing element

INFO!
Do not use pointed or sharp-edged objects to remove the sealing element. They may damage the sealing element or the bead.
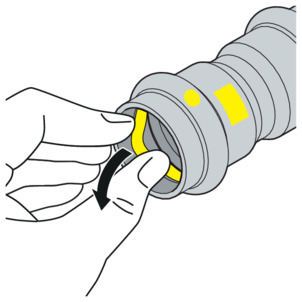
-
Remove the sealing element from the bead.
Inserting the sealing element
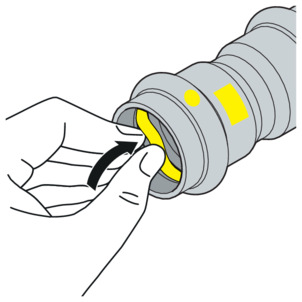
-
Insert a new, undamaged sealing element into the bead.
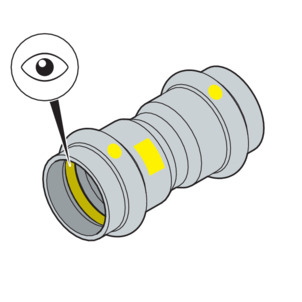
-
Ensure that the complete sealing element is in the bead.
Bending pipes
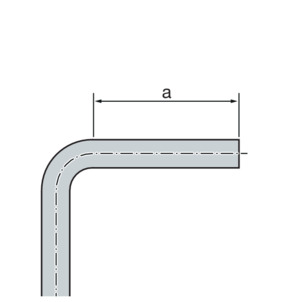
Pipes in the sizes d15, 18, 22 and 28 can be bent cold with commercially available bending equipment (radius at least 3.5 x d).
The pipe ends (a) must be at least 50 mm long so that the press connectors can be mounted properly.
Cutting pipes to length

NOTICE!
Leaking press connections due to damaged material!
Press connections can become leaky due to damaged pipes or sealing elements.
Observe the following instructions to avoid damage to pipes and sealing elements:
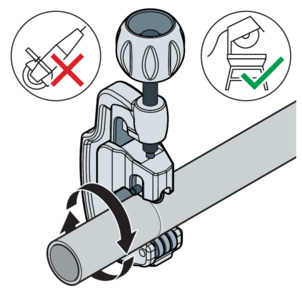
Do not use cutting discs (angle grinders) or flame cutters when cutting to length.
Do not use grease or oils (e. g. cutting oil).
For information about tools, also see Required tools .
-
Cut the pipe at a right angle as accurately as possible using a pipe cutter or a fine-toothed hacksaw to ensure a complete and even pipe insertion depth.
Avoid grooves on the pipe surface.
Stripping pipes
When dealing with coated pipes, the plastic coating must be removed from the area around the press connections by means of a chamfer (model 1158).
The use of other chamfer tools is not permitted.
-
Remove coating from the pipe end using a chamfer.
-
The length of the stripped pipe end corresponds to the insertion depth of the press connector.

INFO!
Do not sharpen the blades of the chamfer, replace the blades.
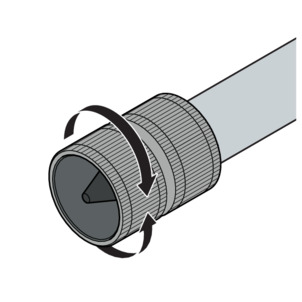
Deburring the pipes
The pipe ends must be thoroughly deburred internally and externally after shortening.
Deburring prevents the sealing element being damaged or the that the press connector cants when mounted. Viega recommends using a deburrer (model 2292.2).

NOTICE!
Damage due to the wrong tool!
Do not use sanding disks or similar tools when deburring. The pipes could be damaged by these.
-
Deburr the inside and outside of the pipe.
Pressing the connection

Requirements:
The pipe end is not bent or damaged.
The pipe is clean.
The pipe is deburred.
The correct sealing element is in the press connector.
HNBR = yellow
The sealing element is undamaged.
The complete sealing element is in the bead.
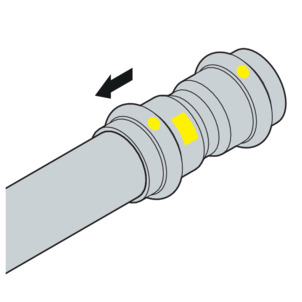
-
Push the press connector onto the pipe as far as it will go.
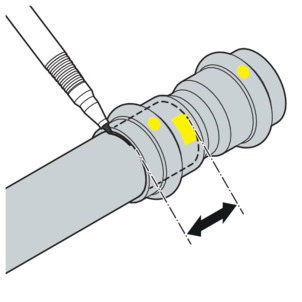
-
Mark the insertion depth.
-
Place the press jaw onto the press machine and push the retaining bolt in until it clicks into place.
INFO!Observe the press tool instruction manual.
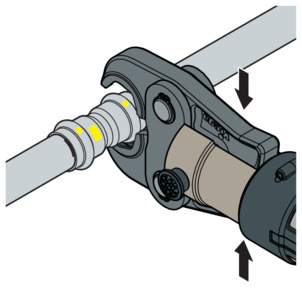
-
Open the press jaw and place it at a right-angle onto the press connector.
-
Check the insertion depth using the marking.
-
Ensure that the press jaw is placed centrally on the bead of the press connector.
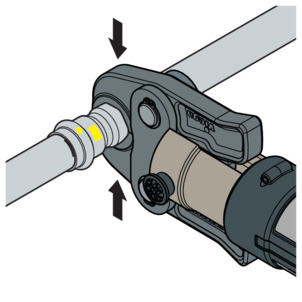
-
Carry out the pressing process.
-
Open and remove the press jaw.
-
Connection is pressed.
Flange connections
In the press connector system shown, flange connections in sizes 22 to 54 mm are possible.
The assembly of flange connections may only be carried out by qualified personnel. Personnel can be qualified to assemble flange connections on the basis of applicable directives, for example; see Regulations from section: Establishing a flange connection .
A corresponding training section on proper flange connection assembly in vocational training (of staff/specialist personnel) with qualified completion as well as successful regular application are considered as sufficient proof.
Other employees without the appropriate technical training (e.g. operating personnel) who are to install flange connections must be provided with technical knowledge through training measures (theoretical and practical); this must be documented.
washers
The advantages of using hardened washers are:
Defined friction surface during assembly.
Defined unevenness in calculation and thus reduction of the scattering of the tightening torque, whereby a greater hexagon screw force can be achieved mathematically.
Flange types
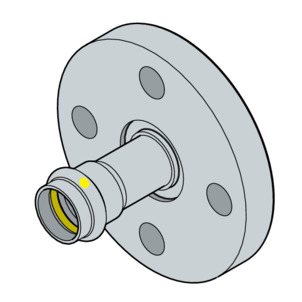
Fixed flange
Steel, stainless
Press connection made of stainless steel
Model 0259: 22 to 54 mm
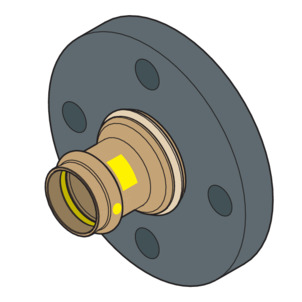
loose flange
Steel, black, powder-coated
Press connection made of gunmetal or silicon bronze
Model 2659.5: 28 mm
Establishing a flange connection

INFO!
Always make the flange connection first and then the press connection.
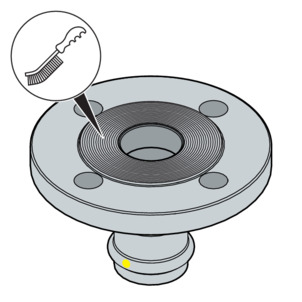
-
If necessary, remove any temporary coatings on the flange sealing surfaces without leaving any residue before assembly, using cleaning agents and a suitable wire brush.
NOTICE!When replacing seals, make sure to remove the old seal completely from the flange sealing surface without damaging the flange sealing surface.
-
Ensure that the flange sealing surfaces are clean, undamaged and even. In particular, there must not be any radial surface damage such as grooves or impact marks.
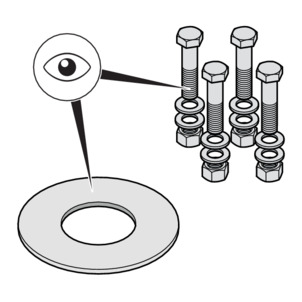
-
The hexagon screws, nuts and washers must be clean and undamaged and comply with the specifications for minimum hexagon screw length and strength class, see Required tightening torques .
-
During disassembly, replace removed hexagon screws, nuts and washers with new ones if damaged.
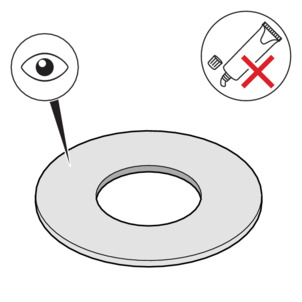
-
The seal must be clean, undamaged and dry. Do not use adhesives and assembly pastes for seals.
-
Do not reuse used seals.
-
Do not use seals with kinks as they pose a safety risk.
-
Ensure that seals are free from faults and defects and that the manufacturer's specifications are complied with.
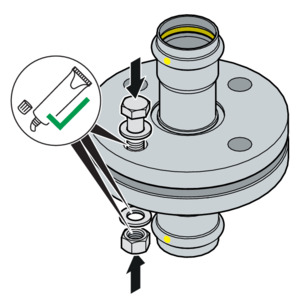
-
Lubricate the following flange elements with suitable lubricant:
Hexagon screw thread
Washer
Nut support
NOTICE!Observe the manufacturer's information on the application and temperature range of the lubricant.
Install and centre the sealing element
The correct assembly of flange connections requires parallel aligned flange blades without an offset centre that allow the sealing element to be inserted in the correct position without damage.
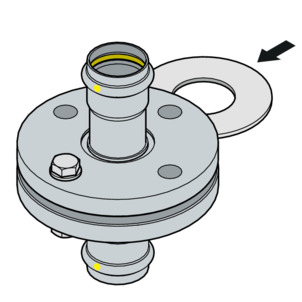
-
Press the sealing surfaces far enough apart so that the seal can be inserted without force and without damage.
The gap (out-of-parallelism of the sealing surfaces) before tightening the hexagon screws is not critical if the permissible gap is not exceeded.
DN | Permissible gap a-b [mm] |
|---|---|
20–25 | 0.4 |
32–50 | 0.6 |
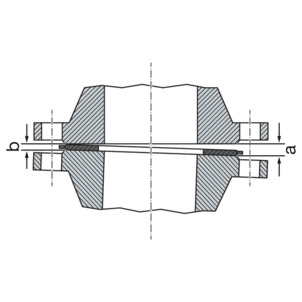
-
Remove the gap from the gaping side (a).
-
In case of doubt, tighten the flanges without inserting a seal by tightening the hexagon screws to achieve parallelism and a sealing surface distance of approx. 10 % of the nominal torque.
-
The gap is not permissible if the flange position cannot be achieved without great effort.
Systematics for tightening hexagon screws
The order in which the hexagon screws and nuts are tightened has a significant influence on the force distribution acting on the seal (surface pressure). Incorrect tightening leads to a high dispersion of the pretensioning forces and can result in the required minimum surface pressure not being reached and even in leaks.
After tightening the nut, at least two but no more than five threads should protrude from the end of the hexagon screw.
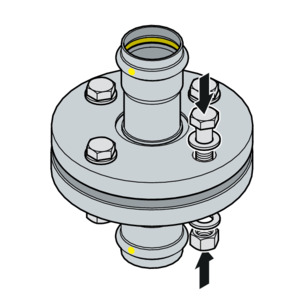
-
Prepare the hexagon screws by hand, observing the following:
Install the hexagon screws so that all the hexagon screw heads are on one flange side.
For horizontally arranged flanges, insert the hexagon screws from above.
Replace stiff hexagon screws with easy-running ones.
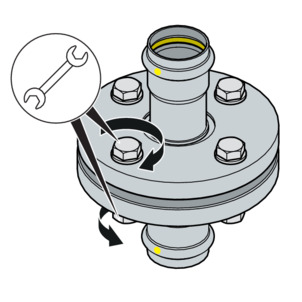
-
The simultaneous use of several tightening tools is possible.
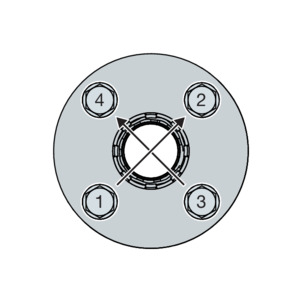
Suit order
-
Tighten all hexagon screws crosswise with 30 % of the nominal tightening torque.
-
Tighten all hexagon screws as described in step 1 with 60 % of the nominal tightening torque.
-
Tighten all hexagon screws as described in step 1 with 100 % of the nominal tightening torque.
-
Tighten all hexagon screws again with the full nominal tightening torque. Repeat this process until the nuts can no longer be turned when the full tightening torque is applied.
Required tightening torques
Tightening torques for Sanpress Inox G flange adapters PN 10/16
Model | DN | Article number | Thread | Min. required tightening torque [Nm] | Max. permissible tightening torque [Nm] | Hexagon screw length [mm] | Strength class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0259 | 20 | 735 777 | M12 | 38 | 50 | 60 | A2 - 70 |
25 | 735 784 | 48 | |||||
32 | 735 791 | M16 | 69 | 125 | 70 | ||
40 | 735 807 | 76 | |||||
50 | 735 814 | 87 | |||||
2659.5 | 25 | 490 669 | M12 | 48 | 50 | 65 | A2 - 70 |
Disconnecting the flange adapter
Before starting to disassemble an existing flange connection, get approval and a work permit from the responsible company, if necessary, observing the following:
The system section must be depressurised and completely flushed.
Secure built-in or attached parts that are not held separately before loosening the flange connection. This also applies to fastening systems such as spring hangers and supports.
Start loosening hexagon screws or nuts on the side facing away from the body, loosen the remaining hexagon screws slightly and only disassemble completely when you have ensured that the piping system does not present a risk. If a pipeline is under tension, there is a risk of the pipeline rupturing.
Loosen the hexagon screws or nuts crosswise in at least two passes.
Close open ends of strands with dummy plugs.
Transport disassembled pipelines only in closed condition.
When replacing seals, make sure to remove the old seal completely from the flange sealing surface without damaging the flange sealing surface.

NOTICE!
Caution when using an angle grinder!
When loosening defective hexagon screws and nuts with the help of an angle grinder, sparks are produced that can burn into the pipe material and cause corrosion.
Leakage test
The installer must perform a leakage test before commissioning.
Only carry out this test with suitable, tested and approved equipment.
Carry out this test on a system that is finished but not covered.
Observe the applicable regulations, see Regulations from section: Leakage test .
Document the result.

NOTICE!
Multiple pressing or re-pressing of a leaking press connection is not permitted.
Maintenance
The gas installation must be given a visual inspection, e. g. by the owner, once a year.
Serviceability and leak tightness must be checked every twelve years by an installation contractor.
To be covered by the warranty and to ensure the safe operation of the gas installations, operate and maintain them as intended, see Regulations from section: Maintenance .
Disposal
Separate the product and packaging materials (e. g. paper, metal, plastic or non-ferrous metals) and dispose of in accordance with valid national legal requirements.